

By Gu Siyu
On May 19, the World Health Organization announced that it has granted an emergency use authorization for Convidecia, a coronavirus vaccine made by China's CanSino Biologics.
It makes Convidecia the 11th COVID-19 vaccine to gain access to the global market and the third such Chinese product following vaccines made by Sinopharm and Sinovac Biotech, which got WHO approval last year.
As the coronavirus infections continue to spread across the world, equitable access to safe and effective vaccines is believed to be a game-changing tool against the pandemic.
China is now the world’s largest provider of COVID-19 vaccines. Its total supply has exceeded that of any other country in the world by far. At the end of March this year, Sinovac topped the list of vaccine doses delivered globally, the IMF-WHO vaccine data base showed.
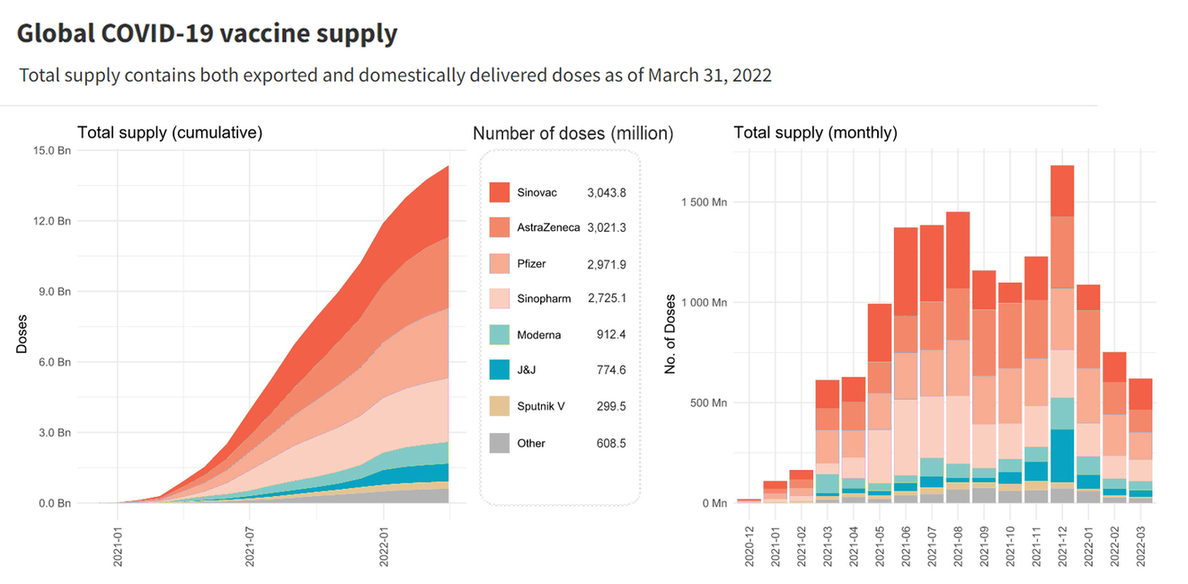
Since the out break of the pandemic, China has proactively answered the call of WHO in promoting vaccine development, manufacturing and deployment. As it steps up the public health efforts, China's role in international cooperation on pandemic prevention and control has proven multifaceted and crucial today.
Guarantor of global public goods
Amid growing concerns about countries putting national interests before the quest for life-saving vaccines, China has pledged to make its COVID-19 vaccines a global public good. The vaccines are provided to other developing countries on a priority basis to ensure wider vaccine accessibility and affordability in the world.

By far, more than 2.2 billion doses of Chinese COVID-19 vaccines have been provided to over 120 countries and international organizations, most of which are developing countries, new official data showed. More countries are mainly using Chinese vaccines to fight against this pandemic.
Vaccine doses were secured through different channels, including bilateral agreements with manufacturers, direct donations and multilateral agreements through the COVAX facilities and other institutions. Figure below shows bilateral deals signed between countries and Chinese vaccine companies based on IMF-WHO statistics.
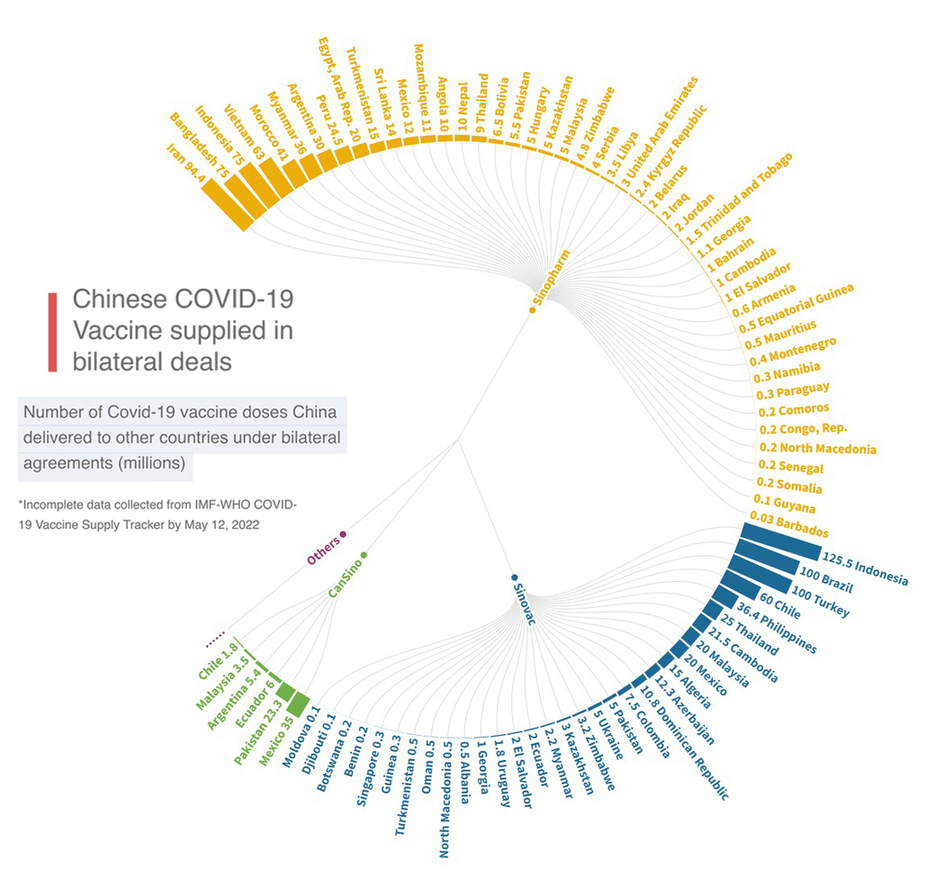
In general, China has supplied COVID-19 vaccines to countries in four geographical regions - the Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Africa and Europe. While the Asia-Pacific has received the largest number of Chinese vaccines, Africa has more than 20 countries receiving vaccines from China through bilateral deals.
Africa has the most countries to see total vaccine deliveries from China following the latter’s commitment to provide another 1 billion doses of vaccines to the region at the 8th FOCAC Ministerial Meeting that took place last year.
Vaccines are delivered as global public goods with auxiliary materials including 4.6 billion protective gowns and more than 430 billion face masks to 153 countries and 15 international organizations, according to data updated by early May.
China has also sent 37 medical expert teams to 34 countries and shared COVID-19 prevention and control experience with over 180 countries and international organizations.
Driver of vaccine capacity and innovation
“In the process of jointly advancing vaccination, China has become an important force in addressing the global vaccine distribution deficit and closing the immunity gap. This is due to increasing innovation and production capabilities, as well as a growing commitment to global cooperation”, noted experts at the 2022 Annual Conference of the Boao Forum for Asia in April.
Supporting vaccine companies in conducting joint R&D and production with developing countries is part of the Global Vaccine Cooperation Action Initiative that Chinese President Xi Jinping proposed last year. Through cooperative productions with more than 20 countries in the world, China has now built up an annual production capacity of 1 billion vaccine doses overseas.
The latest report released by the World Intellectual Property Organization shows that China was among the pacesetters of COVID-19 vaccine and therapeutics innovation during the the early months of the pandemic.
In the first 21 months of the pandemic, close to 5,300 patent applications relating to COVID-19 were filed across 49 patent offices. This included nearly 1,500 filings related to therapeutics and over 400 filings related to vaccines.
The greatest number of COVID-19 patent filings for vaccines were found in China, which accounted for more than half of the global total. It was followed by the US, the Russian Federation, the UK, Republic of Korea, Germany, India, Austria, Switzerland and Australia.
China was also a top origin of COVID-19 therapeutic technologies along with the U.S. and India. According to application profile, corporates, research organizations and universities filed the most patents from China.
The report also highlights institutions worked together with private industry to speed the development of life-saving COVID-19 vaccines and therapeutics, and confirms that accelerated innovation and vaccine development during the pandemic were possible thanks to pre-pandemic research breakthroughs and technological advancements.
Contributor to global vaccine equity
As the world’s pace of vaccination picks up, the latest statistics show that more than 67% of the world population has been vaccinated against COVID-19. However, a wide gap in vaccination rates is observed among different countries and groups.
While more than 70% of the population have received vaccines in high-income countries, only 15.21% of people in low-income countries have been vaccinated with at least one dose, and just over 5% have been fully vaccinated. The prominent disparity indicates that the global immunity gap remains a pressing issue hindering the human anti-pandemic process.
China has ramped up efforts for more equitable distribution of vaccines. Efficient measures, including scaling up vaccine supply and promoting technology sharing for joint production overseas, have been strengthened to improve vaccine accessibility, especially for vulnerable groups. It is also among the major donors of vaccines to low- and middle-income countries.
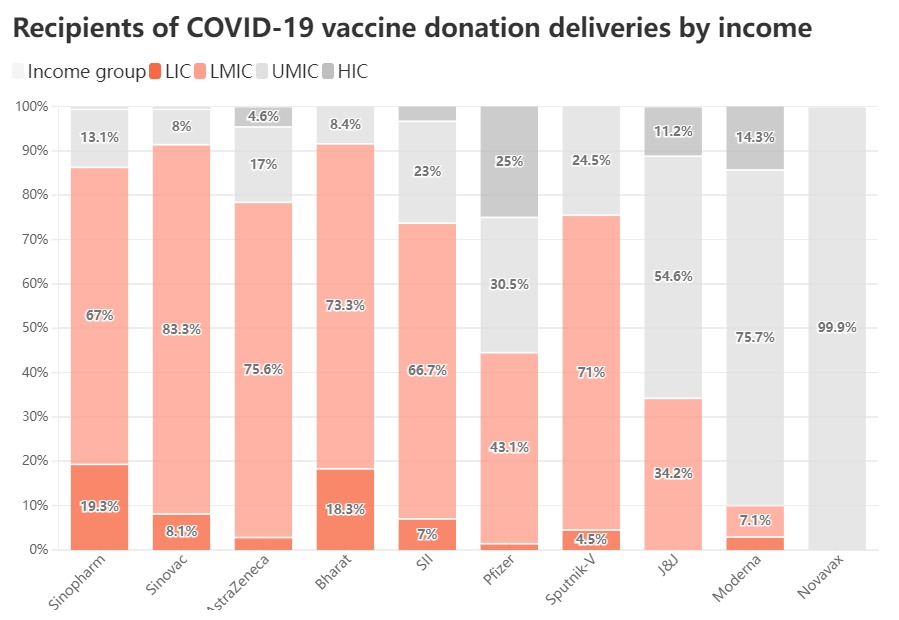
An IMF-WHO database has recorded the number of COVID-19 vaccine doses delivered through direct donations via related facilities since the outbreak of the pandemic. Analysis of the data shows that among the 10 vaccines with WHO EUL approval, China’s Sinopharm and Sinovac vaccines had the largest proportion of vaccine donations to low-income countries (LIC) and lower-middle-income countries (LMIC) respectively.
As China has taken part in COVAX and ACT-A under the WHO framework, it has also donated $100 million to COVAX for the distribution of vaccines to developing countries so far.
China's strenuous efforts for more equitable vaccine distribution indicate an active role it plays in narrowing the global immunity gap. In the face of the recurrent waves of the pandemic, the UN stressed more resilient and resolved global responses to current and future challenges.
Practically, China is securing vaccine supply as a commitment to facilitate the anti-pandemic cooperation under the multilateral framework and make contributions to mankind's early victory over the pandemic.
[1]This chart shows recipient countries of Chinese COVID-19 vaccines delivered through direct donation. *Incomplete data collected from IMF-WHO COVID-19 vaccine tracker by May 12, 2022.
点击右上角![]() 微信好友
微信好友
 朋友圈
朋友圈

请使用浏览器分享功能进行分享
